Online
All Product Categories
Overhead insulated wire
Aluminum and aluminum alloy conductors are low in cost and light in weight, and are widely used in medium and low voltage overhead lines.
Overhead insulated wire
Aluminum and aluminum alloy conductors are low in cost and light in weight, and are widely used in medium and low voltage overhead lines.
Other Product Cases
Step 1
Chip Count
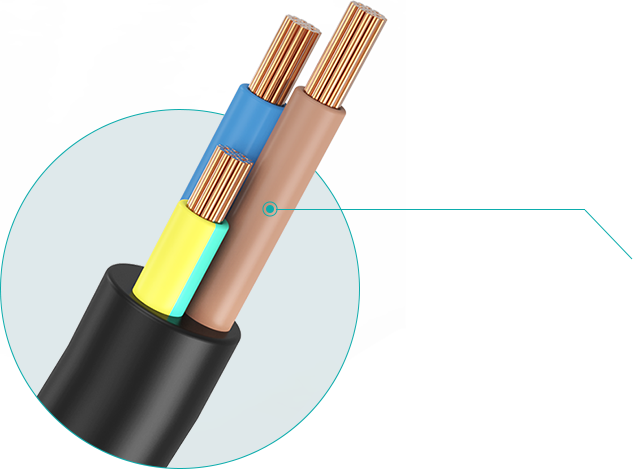
1 core 10 square -630 or customized
Step 2
Features
01
Improve power supply safety
- The insulation layer can effectively prevent short circuits and grounding faults caused by direct contact between the wires and trees, buildings and other objects, reduce power outages caused by foreign objects touching, and improve the reliability of power supply.
- It can reduce the risk of electric shock for line maintenance personnel and ensure the personal safety of operation and maintenance personnel.
02
Reduce the width of the line corridor
- Since insulated wires can reduce the arcs caused by phase-to-phase short circuits and grounding faults, the phase-to-phase distance of the line and the distance between the wires and the ground and other objects can be appropriately reduced, thereby saving the floor space of the line corridor.
03
Reduce electromagnetic interference
- Compared with bare wires, the electromagnetic field distribution of overhead insulated wires is more concentrated, and the electromagnetic interference to the outside world is relatively small. It has advantages in some areas with high requirements for the electromagnetic environment (such as areas near communication lines, electronic equipment, etc.).
04
Good corrosion resistance
- The insulation layer plays a certain protective role on the wires, protecting them from direct erosion by the external environment (such as acid rain, humid air, etc.), and extending the service life of the wires.
Step 3
Specs
| Item | 1KV Overhead Insulated Wire | 10KV Overhead Insulated Wire |
| Rated voltage | 1kV (kilovolt) | 10kV (kilovolt) |
| Conductor material | Copper, aluminum | Copper, aluminum |
| Insulation material | Polyethylene (PE), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), etc. | Polyethylene (PE), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) |
| Conductor specification | 1.5mm² ~ 300mm² | 16mm² ~ 400mm² |
| Conductor structure | Single or stranded structure | Single or stranded structure |
| Rated current | 10A ~ 500A (depending on the cross section and ambient temperature) | 50A ~ 1000A (depending on the cross section and ambient temperature) |
| Operating temperature | -40°C to +90°C | -40°C to +90°C |
| Short circuit temperature | 250°C (under short circuit) | 250°C (under short circuit) |
| Insulation withstand voltage | 2.5kV (test voltage) | 20kV (test voltage) |
| Protection level | IP43 ~ IP65 (depending on the outer sheath material) | IP43 ~ IP65 (depending on the outer sheath material) |
| Outer sheath material | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or other UV-resistant and weather-resistant materials | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or other UV-resistant and weather-resistant materials |
| Maximum allowable tension | 500N ~ 2000N (depending on the conductor specification) | 1500N ~ 4000N (depending on the conductor specification) |
| Cable bending radius | 15 times the wire diameter | 15 times the wire diameter |
Step 4
Combo
WhatsApp
Email
WeChat
WhatsApp
Email
WeChat
Contact
You can contact us through the following four methods, and we will get in touch with you immediately after receiving your inquiry!
Call us
Send Email
Leave a Message
Add WeChat or WhatsApp