Online
All Product Categories
Low voltage control cable 300/500V-shielded
With good insulation performance, it can ensure the insulation between the core wires and between the core wires and the outside world in different working environments
Low voltage control cable 300/500V-shielded
With good insulation performance, it can ensure the insulation between the core wires and between the core wires and the outside world in different working environments
Other Product Cases
Step 1
Category
| Voltage | Outer layer | Model | Grade |
| 300/500V | Shielded type |
KVVP KVVRP KVVP2 KVVP3 KYJVP KYJVRP KYJVP2 DJYPVP DJYP2VP2 RVSP |
Flame retardant N fireproof RCA grade |
| Steel tape shielded |
KVVP22 KVVRP22 KVV22 RVV22 KYJVP22 DJYPVP22 DJYP2VP2-22 RVSP22 |
||
| Non-shielded type |
KVV KVVR KYJV KYJVR |
||
| Non-shielded steel tape type |
KVV22 KYJV22 VVR22 |
Step 2
Chip Count
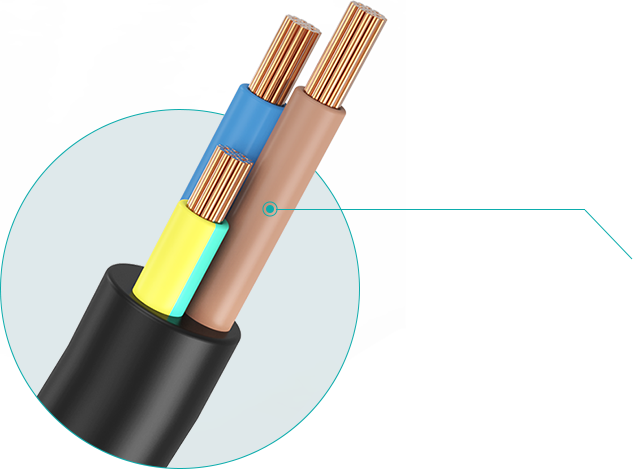
Single core-240 core
Step 3
Features
01
More cores
Control cables need to transmit multiple control signals, so they generally have more cores, usually ranging from 2 to 61 cores. This can meet the transmission needs of different signals in complex control systems. For example, on an automated production line, it may be necessary to simultaneously transmit multiple control signals such as the start, stop, and speed adjustment of the equipment.
02
Low working voltage
It is mainly used to transmit control signals. Its working voltage is usually 450/750V and below. Compared with the high voltage level of power cables, the voltage of control cables is lower.
03
Small conductor cross-section
Since the current transmitted by the control cable is small, the conductor cross-section is generally relatively small, and the common cross-section specification is less than 10 square millimeters.
04
Good shielding performance (some cables)
In some occasions where signal anti-interference requirements are high, the control cable will adopt a shielding structure, such as copper wire braided shielding, aluminum foil shielding, etc., which can effectively prevent the influence of external electromagnetic interference on the control signal and ensure the accuracy and stability of signal transmission.
05
Good insulation performance
With good insulation performance, it can ensure the insulation between the core wires and between the core wires and the outside world under different working environments, reducing the probability of faults such as leakage and short circuit.
06
Good heat resistance and cold resistance (some cables)
According to the requirements of different application scenarios, some control cables have good heat resistance and cold resistance and can work normally in high or low temperature environments.
07
Good flexibility
Control cables may need to be bent and laid during installation, so they need to have good flexibility to facilitate construction and reduce mechanical damage to the cables during installation.
Step 4
Specs
| Technical Parameters | Description |
| Cable type |
Insulation material: polyvinyl chloride (PVC), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) Conductor type: copper conductor or aluminum conductor |
| Voltage level | Rated voltage: 300/500V |
| Conductor specifications | 0.5 mm²、1.0 mm²、1.5 mm²、2.5 mm²、4 mm²、6 mm²、10 mm² |
| Insulation material | Insulation material: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) Insulation layer thickness: 0.6 mm - 2.0 mm |
| Sheath material |
Sheath material: PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PE (polyethylene) Sheath thickness: 1.0 mm - 2.5 mm |
| Current carrying capacity |
0.5 mm²: about 3 A 1.0 mm²: about 6 A 1.5 mm²: about 10 A 2.5 mm²: about 16 A 4 mm²: about 20 A 6 mm²: about 25 A |
| Temperature range |
Operating temperature: -15°C to +70°C Rated temperature: 70°C |
| Tensile strength | Tensile strength ≥ 15 MPa |
| Protection level | Common protection level: IP65 (waterproof, dustproof, suitable for outdoor environment) |
| Service life | Service life ≥ 25 years |
| Standard | International standards such as GB/T 9330, IEC 60227, UL, BS |
| Application scenarios | Suitable for low voltage control, signal transmission, power transmission, etc., widely used in industrial equipment, power facilities, automation control systems, instrument connections, etc. |
WhatsApp
Email
WeChat
WhatsApp
Email
WeChat
Contact
You can contact us through the following four methods, and we will get in touch with you immediately after receiving your inquiry!
Call us
Send Email
Leave a Message
Add WeChat or WhatsApp